
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Complications
- SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):319-326. Published online September 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0014
- 5,831 View
- 315 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
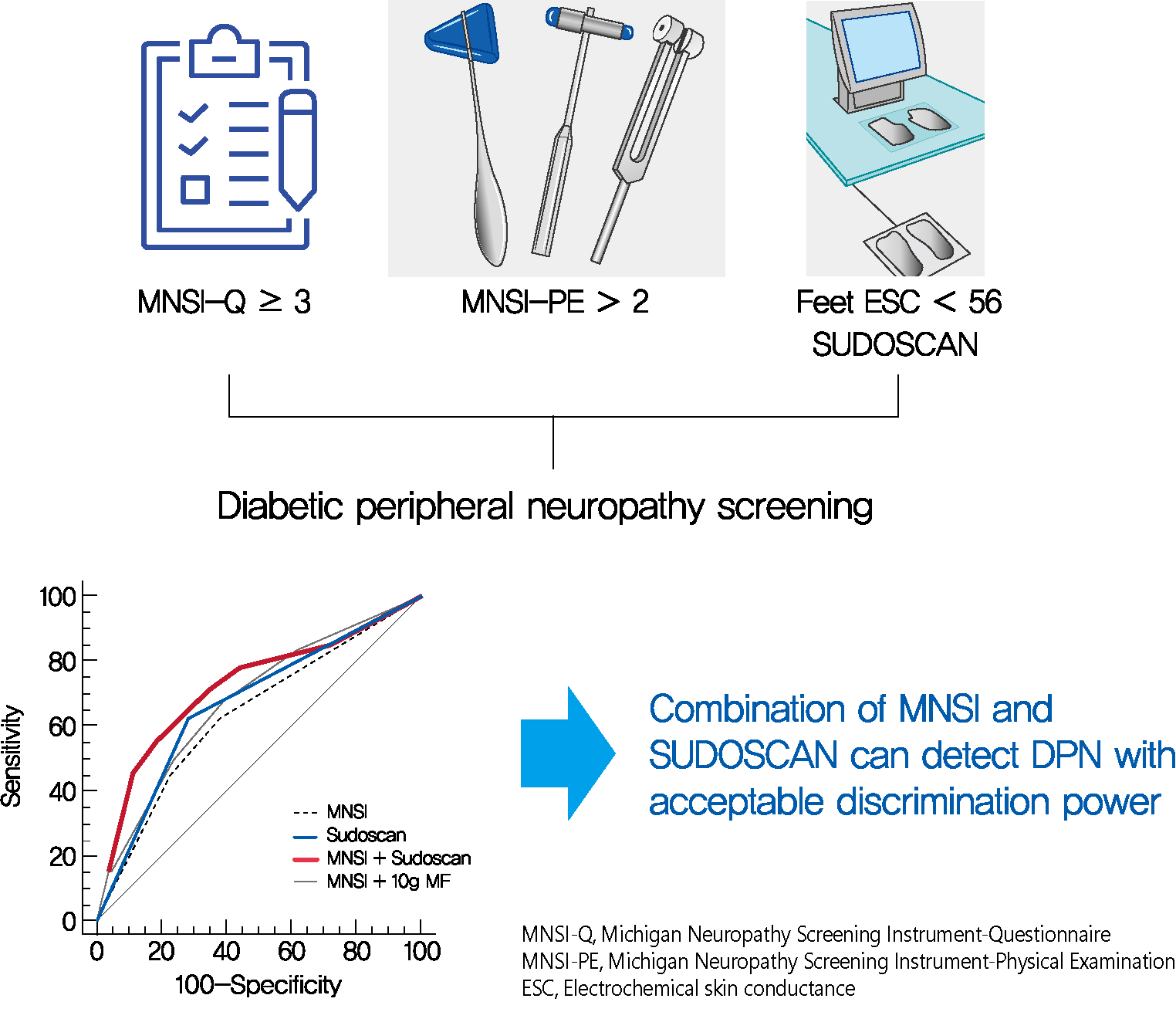
Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is important to prevent severe foot complication, but the detection rate of DPN is unsatisfactory. We investigated whether SUDOSCAN combined with Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) could be an effective tool for screening for DPN in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in clinical practice.
Methods
We analysed the data for 144 people with T2DM without other cause of neuropathy. The presence of DPN was confirmed according to the Toronto Consensus criteria. Electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) of the feet was assessed using SUDOSCAN. We compared the discrimination power of following methods, MNSI only vs. SUDOSCAN only vs. MNSI plus SUDOSCAN vs. MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test.
Results
Confirmed DPN was detected in 27.8% of the participants. The optimal cut-off value of feet ESC to distinguish DPN was 56 μS. We made the DPN screening scores using the corresponding odds ratios for MNSI-Questionnaire, MNSI-Physical Examination, SUDOSCAN, and 10-g monofilament test. For distinguishing the presence of DPN, the MNSI plus SUDOSCAN model showed higher areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) than MNSI only model (0.717 vs. 0.638, P=0.011), and SUDOSCAN only model or MNSI plus 10-g monofilament test showed comparable AUC with MNSI only model.
Conclusion
The screening model for DPN that includes both MNSI and SUDOSCAN can detect DPN with acceptable discrimination power and it may be useful in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ming Wang, Niuniu Chen, Yaxin Wang, Jiaying Ni, Jingyi Lu, Weijing Zhao, Yating Cui, Ronghui Du, Wei Zhu, Jian Zhou
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients by predominantly increasing large-fiber lesions
Sijia Fei, Jingwen Fan, Jiaming Cao, Huan Chen, Xiaoxia Wang, Qi Pan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111585. CrossRef - Early detection of diabetic neuropathy based on health belief model: a scoping review
Okti Sri Purwanti, Nursalam Nursalam, Moses Glorino Rumambo Pandin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Erica Vetrano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Maria Alfano, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, Alessia Piacevole, Giuseppina Tagliaferri, Maria Rocco, Ilaria Iadicicco, Giovanni Docimo, Luca Rinaldi, Celestino Sardu, T
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3554. CrossRef - Screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in resource-limited settings
Ken Munene Nkonge, Dennis Karani Nkonge, Teresa Njeri Nkonge
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of electrochemical skin conductance measurement by Sudoscan® for assessing autonomic dysfunction in peripheral neuropathies beyond diabetes
Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur
Neurophysiologie Clinique.2023; 53(2): 102859. CrossRef - Electrochemical skin conductances values and clinical factors affecting sudomotor dysfunction in patients with prediabetes, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes: A single center experience
Bedia Fulya Calikoglu, Selda Celik, Cemile Idiz, Elif Bagdemir, Halim Issever, Jean-Henri Calvet, Ilhan Satman
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 499. CrossRef - Autonomic Nerve Function Tests in Patients with Diabetes
Heung Yong Jin, Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 71. CrossRef - Validation of the Body Scan®, a new device to detect small fiber neuropathy by assessment of the sudomotor function: agreement with the Sudoscan®
Jean-Pierre Riveline, Roberto Mallone, Clarisse Tiercelin, Fetta Yaker, Laure Alexandre-Heymann, Lysa Khelifaoui, Florence Travert, Claire Fertichon, Jean-Baptiste Julla, Tiphaine Vidal-Trecan, Louis Potier, Jean-Francois Gautier, Etienne Larger, Jean-Pas
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Electrochemical Skin Conductance by Sudoscan in Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Liang-Te Chiu, Yu-Li Lin, Chih-Hsien Wang, Chii-Min Hwu, Hung-Hsiang Liou, Bang-Gee Hsu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 187. CrossRef - The Presence of Clonal Hematopoiesis Is Negatively Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Han Song, Youngil Koh, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 243. CrossRef - Case report: Significant relief of linezolid-induced peripheral neuropathy in a pre-XDR-TB case after acupuncture treatment
Yuping Mo, Zhu Zhu, Jie Tan, Zhilin Liang, Jiahui Wu, Xingcheng Chen, Ming Hu, Peize Zhang, Guofang Deng, Liang Fu
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of sudomotor alterations evaluated by Sudoscan in patients with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Ana Cristina García-Ulloa, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Teresa Enedina Cuatecontzi-Xochitiotzi, Jorge Alberto Ramírez-García, Michelle Díaz-Pineda, Fernanda Garnica-Carrillo, Alejandra González-Duarte, K M Venkat Narayan, Carlos Alberto Aguilar-Salinas, Sergio H
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(6): e003005. CrossRef
- Association of sudomotor dysfunction with risk of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





